Financial turnover is a critical metric for businesses of all sizes and industries. It provides insights into a company’s operational efficiency, market demand, and financial health. We explain what financial turnover is, why it matters for businesses, and how it can be effectively managed and improved.
What is Financial Turnover?
Definition of Financial Turnover
Financial turnover, often simply referred to as turnover, is the total sales or revenue generated by a business within a specific period. It is an essential indicator of business activity and performance, reflecting how much business a company is conducting over time.
Calculating Financial Turnover
To calculate financial turnover, sum the total sales or revenue over the given period. The formula is straightforward:
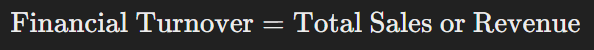
For example, if a business generates £500,000 in sales over a year, its annual financial turnover is £500,000.
Why Financial Turnover Matters
Indicator of Business Performance
Financial turnover is a primary indicator of how well a business is performing. A high turnover suggests strong market demand and efficient operations, while a low turnover may indicate potential problems such as weak demand or operational inefficiencies.
Cash Flow Management
Turnover directly impacts a business’s cash flow. Regular and substantial turnover ensures that there is enough cash inflow to cover expenses, invest in growth opportunities, and meet financial obligations. Managing turnover effectively helps maintain a healthy cash flow, which is crucial for business sustainability.
Investor and Stakeholder Confidence
Investors and stakeholders closely monitor financial turnover as it reflects the business’s ability to generate revenue. Consistent or growing turnover can boost investor confidence and attract additional funding, while declining turnover may raise concerns about the company’s viability.
Planning and Forecasting
Turnover data is vital for business planning and forecasting. By analysing turnover trends, businesses can make informed decisions about inventory management, marketing strategies, and expansion plans. Accurate turnover forecasts enable better preparation for future demand and financial needs.
Components of Financial Turnover
Gross Turnover vs. Net Turnover
It’s important to distinguish between gross turnover and net turnover:
- Gross Turnover: The total sales or revenue generated without deducting any expenses or returns.
- Net Turnover: The total revenue after deducting returns, allowances, and discounts.
Sales Turnover
Sales turnover specifically refers to the revenue generated from sales of goods or services. It excludes other forms of income such as interest or investments. Sales turnover is a critical metric for businesses whose primary revenue comes from selling products or services.
Inventory Turnover
Inventory turnover measures how quickly a company sells its inventory within a given period. It is calculated using the formula:
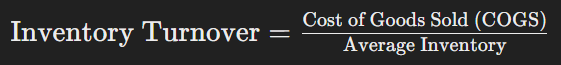
High inventory turnover indicates efficient inventory management and strong sales, while low turnover may suggest overstocking or weak sales.
How to Improve Financial Turnover
Enhance Sales and Marketing Efforts
Increasing sales and marketing efforts can drive higher turnover. This includes:
- Targeted Marketing Campaigns: Focus on reaching the right audience with personalised marketing messages.
- Product or Service Improvements: Enhance the quality and features of products or services to attract more customers.
- Customer Engagement: Build strong relationships with customers through excellent service and loyalty programmes.
Optimise Pricing Strategies
Pricing strategies significantly impact turnover. Consider:
- Competitive Pricing: Analyse competitor pricing and adjust your prices to remain competitive.
- Value-Based Pricing: Set prices based on the perceived value to customers, rather than just cost.
- Promotions and Discounts: Use strategic promotions and discounts to boost sales without eroding profit margins.
Streamline Operations
Efficient operations can lead to higher turnover by reducing costs and improving service delivery. Focus on:
- Inventory Management: Maintain optimal inventory levels to meet demand without overstocking.
- Supply Chain Efficiency: Streamline the supply chain to reduce delays and costs.
- Process Automation: Use technology to automate repetitive tasks, increasing efficiency and reducing errors.
Expand Market Reach
Expanding into new markets can significantly increase turnover. Strategies include:
- Geographical Expansion: Enter new geographic markets where there is demand for your products or services.
- Online Presence: Strengthen your online presence to reach a broader audience through e-commerce platforms.
- Partnerships and Alliances: Form strategic partnerships to tap into new customer bases and distribution channels.
Monitor and Analyse Turnover Data
Regularly monitoring and analysing turnover data helps identify trends, opportunities, and areas for improvement. Use:
- Financial Dashboards: Implement financial dashboards to track turnover metrics in real-time.
- Regular Reviews: Conduct periodic reviews of turnover performance against targets.
- Data Analytics: Use advanced data analytics to gain deeper insights into customer behaviour and market trends.
Common Challenges in Managing Financial Turnover
Seasonal Fluctuations
Many businesses experience seasonal fluctuations in turnover. Managing these fluctuations requires careful planning and inventory management to ensure that demand is met without excessive overstocking during off-peak seasons.
Market Competition
Intense market competition can impact turnover. Businesses need to stay innovative and responsive to market changes to maintain a competitive edge and drive sales.
Economic Factors
Economic conditions, such as recessions or economic booms, can significantly affect turnover. Businesses should develop strategies to mitigate the impact of economic downturns and capitalise on favourable economic conditions.
Customer Preferences
Changing customer preferences can influence turnover. Staying attuned to customer needs and preferences and adapting products or services accordingly is crucial for maintaining and increasing turnover.
Recap
Here’s a quick recap of the key points:
- Definition: Financial turnover is the total sales or revenue generated by a business over a specific period.
- Importance: Turnover is crucial for gauging business performance, managing cash flow, and building investor confidence.
- Components: We differentiated between gross turnover and net turnover, and discussed sales turnover and inventory turnover.
- Improvement Strategies: Enhancing sales efforts, optimizing pricing, streamlining operations, expanding market reach, and monitoring turnover data can help improve financial turnover.
- Challenges: Seasonal fluctuations, market competition, economic factors, and changing customer preferences can impact turnover, but strategic planning can mitigate these challenges.
Managing financial turnover effectively can help businesses thrive and grow, making it a vital metric for success. Stay informed with Turnovr.uk for more insights and strategies.

















Leave a comment