Employee turnover is a natural part of any business, but when turnover rates become excessively high, it can lead to significant financial and operational challenges. This article will analyse the various costs associated with high employee turnover and explore strategies to mitigate these expenses.
Understanding Employee Turnover
Definition of Employee Turnover
Employee turnover refers to the rate at which employees leave an organization and are replaced by new hires. It includes both voluntary turnover (employees resigning) and involuntary turnover (employees being terminated).
Measuring Employee Turnover
To measure employee turnover, use the following formula:
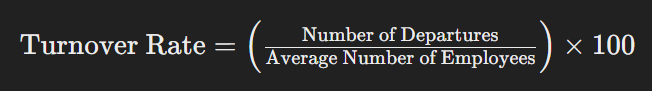
For instance, if a company has an average of 100 employees and 20 leave in a year, the turnover rate is 20%.
Financial Costs of High Employee Turnover
Recruitment Costs
Replacing departing employees involves several expenses, including advertising job openings, recruiting agencies, and hiring temporary staff to cover gaps.
Breakdown of Costs:
- Job Postings: Advertising on job boards and social media platforms.
- Recruitment Agencies: Fees paid to agencies for sourcing candidates.
- Temporary Staff: Costs associated with hiring temporary employees to maintain operations during the recruitment process.
Onboarding and Training Costs
New employees require onboarding and training to get up to speed, which involves both direct and indirect costs.
Breakdown of Costs:
- Training Programs: Expenses for training materials, courses, and trainers.
- Onboarding Time: Time spent by current employees and HR in onboarding new hires.
- Reduced Productivity: Lower productivity levels while new employees learn their roles.
Lost Productivity
High turnover disrupts workflow and decreases overall productivity. It takes time for new employees to reach the productivity levels of their predecessors.
Breakdown of Costs:
- Learning Curve: Time required for new employees to become fully productive.
- Disrupted Teams: Impact on team dynamics and collaboration.
- Project Delays: Delays in project timelines due to staffing changes.
Increased Overtime
When positions are vacant, remaining employees may need to work overtime to cover the additional workload, leading to increased labour costs and potential burnout.
Breakdown of Costs:
- Overtime Pay: Additional wages paid for overtime hours.
- Employee Burnout: Increased risk of burnout leading to further turnover.
Severance and Legal Costs
In cases of involuntary turnover, businesses may incur severance pay and legal costs, especially if the termination process is not handled properly.
Breakdown of Costs:
- Severance Packages: Payments made to departing employees as part of severance agreements.
- Legal Fees: Costs associated with legal disputes or wrongful termination claims.
Operational Costs of High Employee Turnover
Impact on Morale
High turnover can negatively affect the morale of remaining employees, leading to disengagement and further turnover.
Breakdown of Costs:
- Reduced Engagement: Lower employee engagement and motivation.
- Increased Absenteeism: Higher rates of absenteeism due to low morale.
- Team Cohesion: Disruption of team cohesion and dynamics.
Loss of Institutional Knowledge
Departing employees take with them valuable institutional knowledge and experience, which can be difficult to replace.
Breakdown of Costs:
- Knowledge Transfer: Time and effort required to transfer knowledge to new employees.
- Reduced Efficiency: Loss of efficiency due to the absence of experienced staff.
- Customer Relationships: Potential loss of customer relationships built by departing employees.
Customer Satisfaction
Frequent staff changes can lead to inconsistent service and negatively impact customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Breakdown of Costs:
- Service Disruptions: Inconsistencies in service quality due to staff changes.
- Customer Trust: Erosion of customer trust and loyalty.
- Brand Reputation: Negative impact on brand reputation from dissatisfied customers.
Strategies to Mitigate the Costs of High Employee Turnover
Improve Recruitment and Hiring Practices
Investing in better recruitment and hiring practices can help reduce turnover by ensuring a good fit between the company and new employees.
Strategies:
- Thorough Screening: Implement thorough screening processes to identify the best candidates.
- Cultural Fit: Assess candidates for cultural fit to ensure they align with the company’s values and environment.
- Realistic Job Previews: Provide realistic job previews to set accurate expectations.
Enhance Employee Onboarding and Training
Effective onboarding and continuous training can help new employees integrate smoothly and become productive faster.
Strategies:
- Structured Onboarding Programs: Develop structured onboarding programs to guide new hires.
- Mentorship: Pair new employees with experienced mentors for guidance and support.
- Ongoing Training: Offer ongoing training and development opportunities to keep skills updated.
Foster a Positive Work Environment
Creating a positive and supportive work environment can improve employee satisfaction and retention.
Strategies:
- Work-Life Balance: Promote a healthy work-life balance with flexible working options.
- Recognition and Rewards: Implement recognition and rewards programs to acknowledge employee contributions.
- Open Communication: Encourage open communication and feedback between employees and management.
Competitive Compensation and Benefits
Offering competitive salaries and benefits can attract and retain top talent.
Strategies:
- Regular Salary Reviews: Conduct regular salary reviews to ensure competitive compensation.
- Comprehensive Benefits: Provide comprehensive benefits packages, including health insurance, retirement plans, and wellness programs.
- Performance Incentives: Offer performance-based incentives and bonuses.
Career Development Opportunities
Providing clear career development opportunities can motivate employees to stay and grow with the company.
Strategies:
- Training Programs: Offer training programs to develop new skills and advance careers.
- Promotion Paths: Create clear promotion paths and career advancement opportunities.
- Internal Mobility: Encourage internal mobility to allow employees to explore different roles within the company.
Recap
Financial Costs:
- Recruitment and onboarding expenses.
- Lost productivity and increased overtime costs.
- Severance and legal fees.
Operational Costs:
- Negative impact on morale and team cohesion.
- Loss of institutional knowledge and customer relationships.
- Decreased customer satisfaction and brand reputation.
Strategies to Mitigate Costs:
- Improve recruitment and hiring practices.
- Enhance employee onboarding and training.
- Foster a positive work environment.
- Offer competitive compensation and benefits.
- Provide career development opportunities.

















Leave a comment