Managing inventory turnover effectively is crucial for maintaining optimal stock levels, reducing waste, and ensuring smooth business operations. We explore strategies for optimising inventory turnover, helping businesses to balance supply and demand, minimise holding costs, and enhance overall efficiency.
Understanding Inventory Turnover
Definition of Inventory Turnover
Inventory turnover measures how many times a company’s inventory is sold and replaced over a specific period. It is a key indicator of inventory management efficiency.
Importance of Inventory Turnover
- Operational Efficiency: High inventory turnover indicates efficient inventory management and strong sales performance.
- Cost Reduction: Optimising turnover helps reduce holding costs, such as storage and insurance.
- Cash Flow Improvement: Efficient turnover ensures that capital is not tied up in excess inventory, improving cash flow.
Formula
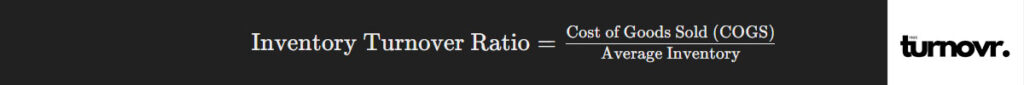
Strategies for Optimising Inventory Turnover
1. Accurate Demand Forecasting
Importance
Accurate demand forecasting helps businesses predict future sales and adjust inventory levels accordingly, preventing overstocking and stockouts.
Strategies
- Historical Sales Data: Analyse past sales data to identify trends and seasonality.
- Market Analysis: Consider market trends, economic conditions, and competitor activities.
- Advanced Forecasting Tools: Use forecasting software and tools to enhance accuracy.
2. Implement Just-In-Time (JIT) Inventory
Importance
JIT inventory systems reduce holding costs by receiving goods only when they are needed for production or sale.
Strategies
- Supplier Relationships: Build strong relationships with reliable suppliers for timely deliveries.
- Inventory Management Systems: Use inventory management software to track inventory levels and reorder points.
- Continuous Monitoring: Regularly monitor inventory levels and adjust orders based on demand fluctuations.
3. Optimise Inventory Levels
Importance
Maintaining optimal inventory levels ensures that businesses have enough stock to meet demand without overstocking.
Strategies
- ABC Analysis: Classify inventory into three categories (A, B, C) based on value and turnover rate. Focus on managing high-value items (A) more closely.
- Economic Order Quantity (EOQ): Calculate the optimal order quantity that minimises total inventory costs, including ordering and holding costs.
- Safety Stock: Maintain a buffer stock to account for demand variability and lead time uncertainties.
4. Regularly Review Inventory Performance
Importance
Regular reviews of inventory performance help identify slow-moving or obsolete items and make informed decisions about inventory management.
Strategies
- Inventory Audits: Conduct periodic audits to assess inventory accuracy and performance.
- Key Performance Indicators (KPIs): Track KPIs such as inventory turnover ratio, stockout rate, and holding costs.
- Slow-Moving Inventory: Identify and address slow-moving inventory by offering promotions or discontinuing products.
5. Implement Inventory Management Technology
Importance
Advanced inventory management technology enhances accuracy, visibility, and control over inventory levels.
Strategies
- Inventory Management Software: Use software to automate inventory tracking, ordering, and reporting.
- Barcode Scanning: Implement barcode scanning for accurate and efficient inventory tracking.
- Real-Time Data: Ensure access to real-time inventory data for better decision-making.
6. Improve Supplier Management
Importance
Effective supplier management ensures timely deliveries and reduces the risk of stockouts or excess inventory.
Strategies
- Supplier Performance: Monitor supplier performance based on delivery times, quality, and reliability.
- Vendor-Managed Inventory (VMI): Partner with suppliers to manage inventory levels and reorder points.
- Diversified Suppliers: Maintain a diversified supplier base to mitigate risks associated with supplier dependence.
7. Streamline Internal Processes
Importance
Efficient internal processes contribute to better inventory management and turnover optimisation.
Strategies
- Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs): Develop and implement SOPs for inventory handling, storage, and management.
- Employee Training: Train employees on inventory management best practices and the use of inventory management systems.
- Process Automation: Automate repetitive tasks to reduce errors and improve efficiency.
Benefits of Optimising Inventory Turnover
Reduced Holding Costs
Optimising inventory turnover minimises holding costs associated with storage, insurance, and obsolescence.
Improved Cash Flow
Efficient turnover ensures that capital is not tied up in excess inventory, improving overall cash flow and financial health.
Enhanced Customer Satisfaction
Maintaining optimal stock levels ensures that products are available when customers need them, enhancing customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Increased Operational Efficiency
Streamlined inventory management processes improve overall operational efficiency and productivity.
Reduced Waste
Efficient inventory turnover reduces the risk of obsolete or expired stock, minimising waste and associated costs.
Recap
- Accurate Demand Forecasting: Use historical sales data, market analysis, and forecasting tools.
- Just-In-Time (JIT) Inventory: Build strong supplier relationships, use inventory management systems, and monitor levels continuously.
- Optimise Inventory Levels: Implement ABC analysis, calculate EOQ, and maintain safety stock.
- Regularly Review Inventory Performance: Conduct audits, track KPIs, and address slow-moving inventory.
- Implement Inventory Management Technology: Use inventory software, barcode scanning, and access real-time data.
- Improve Supplier Management: Monitor supplier performance, consider VMI, and diversify suppliers.
- Streamline Internal Processes: Develop SOPs, train employees, and automate tasks.

















Leave a comment