Employee turnover rate is a crucial metric for any business, providing insight into workforce stability and employee satisfaction. Knowing how to calculate this rate and interpreting what it means for your business can help you develop strategies to retain talent and improve your organisation’s health. This guide will walk you through the steps of calculating employee turnover rate and explain its significance.
What is Employee Turnover Rate?
Definition
Employee turnover rate is the percentage of employees who leave an organization over a specific period, typically a year. It includes both voluntary turnover (employees who resign) and involuntary turnover (employees who are terminated).
Importance
Understanding your employee turnover rate is essential for:
- Identifying Trends: Spotting patterns in employee departures can help identify underlying issues.
- Evaluating Retention Strategies: Measuring the effectiveness of your employee retention strategies.
- Benchmarking: Comparing your turnover rate with industry standards to gauge your company’s performance.
How to Calculate Employee Turnover Rate
Step-by-Step Guide
Step 1: Determine the Time Period
First, decide the time period over which you want to calculate the turnover rate. Most businesses calculate it annually, but you can also assess it monthly or quarterly.
Step 2: Calculate the Average Number of Employees
To find the average number of employees, add the number of employees at the beginning of the period to the number at the end of the period, then divide by two.

For example, if your company had 200 employees at the start of the year and 180 employees at the end of the year:

Step 3: Count the Number of Departures
Next, count the total number of employees who left the company during the period. This includes both voluntary and involuntary departures.
Step 4: Calculate the Turnover Rate
Use the following formula to calculate the turnover rate:
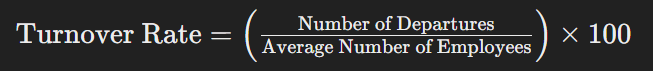
If 30 employees left during the year, the turnover rate would be:
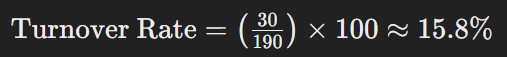
Interpreting the Turnover Rate
High Turnover Rate
A high turnover rate indicates that a large percentage of employees are leaving your company. This can suggest problems such as:
- Low Job Satisfaction: Employees may be unhappy with their roles, management, or work environment.
- Inadequate Compensation: Employees might leave for better-paying jobs elsewhere.
- Lack of Career Development: Limited opportunities for growth can drive employees to seek advancement elsewhere.
Low Turnover Rate
A low turnover rate generally indicates a stable workforce, which can be positive. However, it could also suggest:
- Complacency: Employees may feel secure but uninspired.
- Limited Fresh Ideas: A very low turnover can result in a lack of new perspectives and innovation.
Industry Benchmarks
Comparing your turnover rate to industry benchmarks can provide context. Different industries have varying average turnover rates. For example, retail and hospitality typically have higher turnover rates compared to sectors like healthcare or education.
Factors Influencing Employee Turnover
Internal Factors
- Work Environment: A positive, supportive work environment can reduce turnover.
- Management Practices: Effective leadership and clear communication can improve employee retention.
- Career Opportunities: Providing career advancement opportunities can encourage employees to stay.
External Factors
- Economic Conditions: Economic downturns may reduce turnover as employees are less likely to leave their jobs.
- Labour Market: In a competitive job market, employees may frequently move between jobs for better opportunities.
Strategies to Reduce Employee Turnover
Improve Job Satisfaction
- Regular Feedback: Conduct regular feedback sessions to understand employee concerns and address them promptly.
- Work-Life Balance: Promote a healthy work-life balance through flexible working hours and remote work options.
Competitive Compensation
- Salary Reviews: Regularly review and adjust salaries to ensure they are competitive within your industry.
- Benefits Packages: Offer comprehensive benefits, including health insurance, retirement plans, and wellness programs.
Career Development
- Training Programs: Provide ongoing training and professional development opportunities.
- Promotion Opportunities: Create clear paths for career advancement within the organization.
Enhance Work Environment
- Positive Culture: Foster a positive and inclusive workplace culture.
- Team Building: Organize team-building activities to strengthen relationships among employees.
Recap
- Definition: Employee turnover rate is the percentage of employees who leave an organization over a specific period.
- Calculation:
- Determine the time period.
- Calculate the average number of employees.
- Count the number of departures.
- Use the turnover rate formula.
- Interpretation:
- High turnover rate indicates potential issues with job satisfaction, compensation, or career development.
- Low turnover rate suggests stability but may also indicate complacency.
- Factors Influencing Turnover: Both internal (work environment, management practices) and external (economic conditions, labour market) factors play a role.
- Strategies to Reduce Turnover: Improve job satisfaction, offer competitive compensation, provide career development opportunities, and enhance the work environment.

















Leave a comment