Employee turnover is a significant concern for businesses across various industries. Understanding how turnover rates differ by industry can help organisations develop targeted strategies to retain employees and improve overall workforce stability. This article explores employee turnover trends in different industries and the factors that influence these variations.
Understanding Employee Turnover
Definition
Employee turnover refers to the rate at which employees leave an organisation and are replaced by new hires. It includes both voluntary turnover (employees choosing to leave) and involuntary turnover (employees being terminated).
Measuring Employee Turnover
To measure employee turnover, use the following formula:
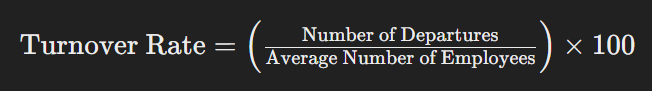
Employee Turnover in Various Industries
Retail
High Turnover Rates
The retail industry is known for having one of the highest turnover rates. This is often due to the prevalence of part-time and seasonal work, lower wages, and limited career advancement opportunities.
Factors Influencing Turnover
- Seasonal Employment: High turnover during peak seasons like holidays.
- Low Wages: Compensation often does not meet employee expectations.
- Limited Benefits: Lack of comprehensive benefits packages.
- Work Environment: High-stress levels due to customer interactions and long hours.
Hospitality
High Turnover Rates
Similar to retail, the hospitality industry experiences high turnover rates. This sector includes hotels, restaurants, and entertainment venues, where job demands are high and working conditions can be challenging.
Factors Influencing Turnover
- Work Hours: Irregular and long working hours, including nights and weekends.
- Stressful Conditions: High-pressure environments with demanding customer service expectations.
- Low Compensation: Wages and benefits often do not match the job demands.
- Seasonal Employment: High turnover during peak tourist seasons.
Healthcare
Moderate to High Turnover Rates
The healthcare industry faces moderate to high turnover rates, particularly among nursing staff and support roles. High stress and emotional demands of the job contribute significantly to turnover.
Factors Influencing Turnover
- Job Stress: High levels of stress and emotional exhaustion.
- Burnout: Long hours and high patient loads lead to burnout.
- Compensation: Competitive salaries are crucial but often insufficient to retain staff.
- Career Advancement: Opportunities for growth and specialisation impact retention.
Technology
Lower Turnover Rates
The technology sector generally experiences lower turnover rates compared to retail and hospitality. However, turnover can be high in startups and rapidly growing tech companies.
Factors Influencing Turnover
- Competitive Salaries: Higher-than-average compensation packages.
- Work Environment: Modern, flexible work environments with remote work options.
- Career Opportunities: Ample opportunities for growth and development.
- Company Culture: Strong focus on culture and employee engagement.
Finance and Banking
Moderate Turnover Rates
The finance and banking industry has moderate turnover rates. While compensation is generally competitive, the high-pressure environment can lead to employee burnout.
Factors Influencing Turnover
- Compensation: Competitive salaries and bonuses.
- Job Stress: High-pressure environment with demanding workloads.
- Career Advancement: Opportunities for career progression are critical.
- Work-Life Balance: Importance of maintaining a healthy work-life balance.
Manufacturing
Moderate to High Turnover Rates
The manufacturing industry often faces moderate to high turnover rates, especially in roles involving repetitive tasks and physical labor.
Factors Influencing Turnover
- Work Conditions: Physical demands and safety concerns.
- Compensation: Wages may not reflect the difficulty of the work.
- Job Satisfaction: Repetitive tasks can lead to low job satisfaction.
- Career Opportunities: Limited opportunities for advancement in some roles.
Education
Lower Turnover Rates
The education sector typically has lower turnover rates, especially among tenured faculty. However, turnover can be higher among administrative staff and early-career teachers.
Factors Influencing Turnover
- Job Satisfaction: High levels of job satisfaction among long-term educators.
- Compensation: Salaries vary, but benefits like job security and pensions are significant.
- Work Environment: Positive work environment with supportive administration.
- Career Development: Opportunities for professional development and further education.
Strategies to Manage Employee Turnover
Industry-Specific Approaches
Retail and Hospitality
- Improve Compensation: Offer competitive wages and benefits.
- Enhance Work Environment: Create a positive and supportive work environment.
- Provide Career Development: Offer training and advancement opportunities.
Healthcare
- Support Work-Life Balance: Implement flexible scheduling and reduce workload.
- Address Burnout: Provide resources for stress management and mental health support.
- Career Growth: Offer opportunities for specialisation and advancement.
Technology
- Foster Company Culture: Maintain a strong, positive company culture.
- Flexible Work Options: Provide remote work and flexible hours.
- Competitive Salaries: Ensure compensation packages are attractive.
Finance and Banking
- Manage Job Stress: Implement strategies to reduce workplace stress.
- Career Progression: Offer clear paths for career advancement.
- Work-Life Balance: Encourage a healthy work-life balance.
Manufacturing
- Improve Work Conditions: Enhance safety and ergonomics in the workplace.
- Compensation: Offer competitive wages and benefits.
- Job Satisfaction: Increase job variety and engagement.
Education
- Professional Development: Provide opportunities for further education and training.
- Supportive Environment: Foster a supportive work environment.
- Recognition: Recognise and reward contributions to the institution.
Recap
- Retail and Hospitality: High turnover due to low wages, seasonal work, and stressful environments.
- Healthcare: Moderate to high turnover driven by job stress and burnout.
- Technology: Lower turnover with competitive salaries and positive work environments.
- Finance and Banking: Moderate turnover influenced by job stress and career opportunities.
- Manufacturing: Moderate to high turnover due to work conditions and job satisfaction.
- Education: Lower turnover with high job satisfaction and supportive environments.

















Leave a comment